Radiological Insights into Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2
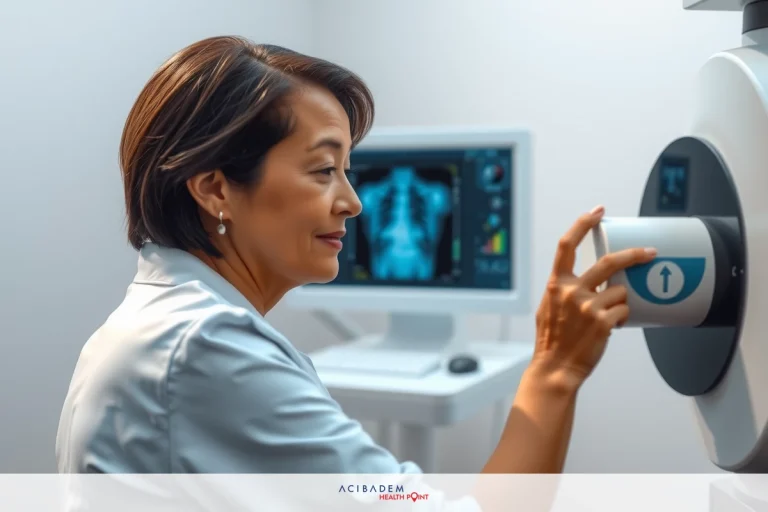
Radiological Insights into Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 is a complex disorder impacting the cerebellum and brainstem, making diagnosis and treatment challenging. Radiological imaging plays a crucial role in its assessment and management.
Advanced imaging is essential for identifying the distinctive characteristics of this condition and making an accurate diagnosis. This section explains how radiology aids in diagnosing Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2.
It highlights the significance of neuroimaging, what clinicians seek during scans, and how it aids in planning diagnosis and treatment. Radiological Insights into Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2
Continue reading to explore the radiologic characteristics of this condition. Imaging plays a key role in diagnosis and management, enhancing understanding of symptoms and informing more effective treatment strategies.
Overview of Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2
Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 is a congenital defect where the cerebellum and brainstem protrude into the spinal canal through the foramen magnum, causing various neurological issues.
Radiological Insights into Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 This condition typically requires specialized tests for diagnosis and treatment.
This condition originates in the womb. After birth, symptoms may include breathing and swallowing difficulties, abnormal eye movements, and muscle weakness. Early detection of these signs is crucial for proper testing.
Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 frequently involves spinal cord problems like cysts or spinal holes. MRI and CT scans assess severity and guide treatment. Radiological Insights into Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2
Radiological Insights into Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 Understanding Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 is essential for grasping its complex diagnostics. Medical professionals need this knowledge to effectively manage and treat affected patients.
Radiologic Features Overview
Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 has distinctive radiologic characteristics that are essential for accurate diagnosis and differentiation from other similar neurological conditions.
A key indicator is the downward displacement of the cerebellar vermis and tonsils visible on imaging scans. This finding is crucial for diagnosing Chiari Malformation Type 2 and distinguishing it from other Chiari types.
Spinal dysraphism, often associated with Chiari Malformation Type 2, indicates spinal abnormalities such as myelomeningocele, which are clearly visible on detailed imaging.
Examining the spine reveals specific issues such as tectal beaking and an elongated medulla, which are crucial for diagnosing Chiari Malformation Type 2. These features assist physicians in accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
| Radiologic Feature | Significance |
|---|---|
| Downward Displacement of Cerebellar Vermis and Tonsils | Key diagnostic marker, helps in identifying Chiari Malformation Type 2 |
| Spinal Dysraphism | Associated with myelomeningocele, essential for complete diagnosis |
| Tectal Beaking | Indicative of Chiari Malformation Type 2, aids in morphological understanding |
| Elongation of Medulla | Critical for assessing the extent of malformation |
Key Imaging Features of Chiari Malformation Type 2
Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 is identifiable on scans by downward displacement of the cerebellar tonsils into the foramen magnum. Additionally, alterations in the brainstem are important diagnostic indicators for medical professionals.
It’s essential to correlate Chiari malformation MRI features with the patient’s symptoms. MRI often shows cerebellar herniation and other posterior skull abnormalities, which may indicate a myelomeningocele—a defect that should be evaluated.
Additional indicators include a stretched or bent appearance of the brainstem, visible on detailed MRI scans. Detecting these changes assists doctors in assessing potential brain impacts and determining the most appropriate treatment.
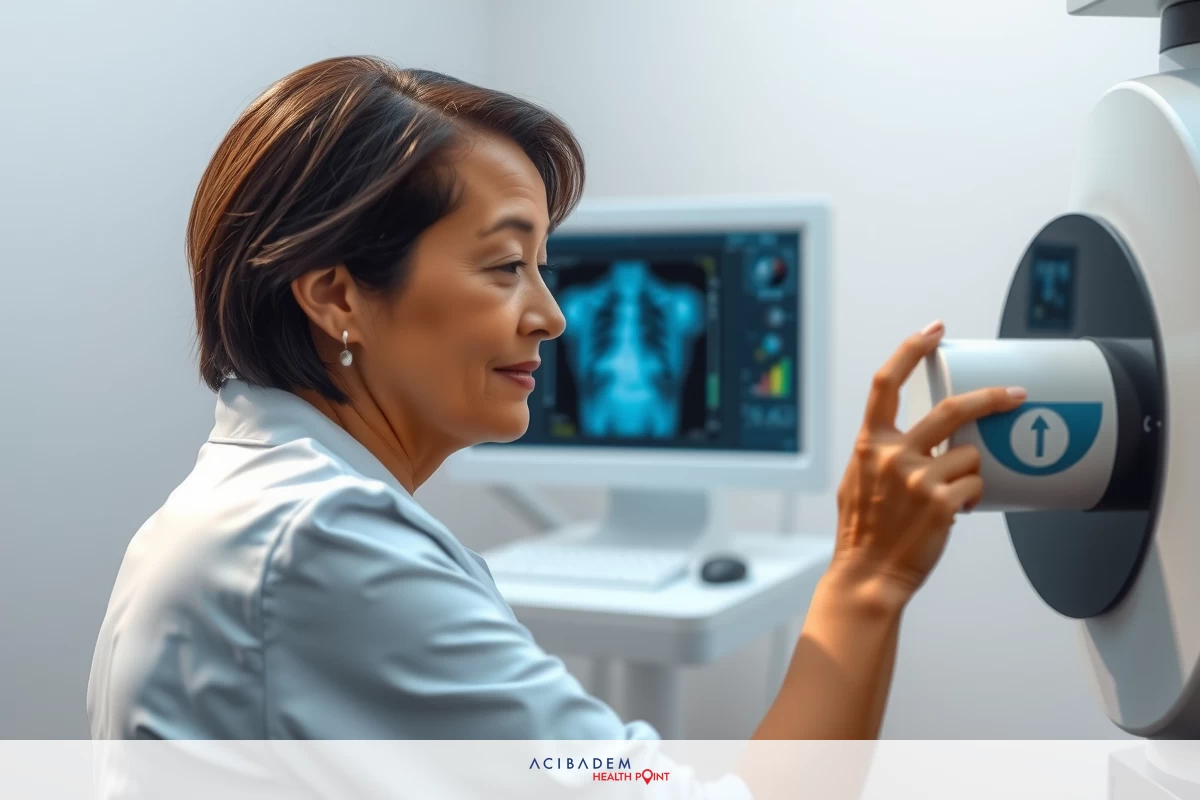
Analyzing Chiari malformation MRI scans allows doctors to assess the extent of cerebellar tonsil and brainstem deformation. These scans are crucial for determining the severity of the condition and guiding appropriate treatment.
Here are the main findings related to Chiari Malformation
Type 2:
| Imaging Finding | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| Cerebellar Tonsillar Herniation | Indicates displacement into foramen magnum |
| Brainstem Deformation | Elongation or kinking of the medulla |
| Neural Tube Defects | Often accompanied by myelomeningocele |
| Posterior Fossa Abnormalities | Downward displacement of cerebellum, possible tight cisterna magna |
The Importance of MRI in Detecting Chiari Malformation Type 2
MRI is essential for diagnosing Chiari Malformation Type 2, providing detailed images of the brain. This enables doctors to better understand the condition and develop effective treatment strategies.
High-Definition Imaging
High-resolution MRI provides detailed images of Chiari Malformation Type 2, allowing for close examination of brain structures. This enables doctors to detect issues that other imaging methods might miss.
Recognizing Critical Anatomical Structures
MRI is essential for identifying critical features of Chiari Malformation Type 2, including abnormalities in the cerebellum and brainstem. It also assesses cerebrospinal fluid flow, which is vital for diagnosis.
Clinical Connection
Doctors combine MRI findings with patient symptoms and other information to diagnose conditions. MRI reveals brain issues, guiding treatment decisions and surgical planning by showing fluid movement.
| Imaging Capability | Significance |
|---|---|
| High-Resolution MRI | Provides detailed visualization of CNS anomalies , aiding in accurate diagnosis. |
| Anatomic Feature Identification | Essential for locating critical brain malformations and understanding structural displacements. |
| Clinical Correlation | Combines imaging data with patient symptoms to inform treatment strategies. |
Role of CT Scanning in Diagnosing Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2
CT scans are essential for diagnosing Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 and are often used alongside MRI. They are particularly valuable when MRI alone doesn’t provide enough information.
Guidelines for When to Use CT Scans
CT scans provide detailed images of the skull’s structure, making them ideal for quick assessment in emergencies. They also clearly depict bones, aiding surgical planning.
Bone Structure Evaluation
CT scans are essential for examining skull anatomy, providing detailed images that reveal subtle bone abnormalities. This aids doctors in diagnosing conditions and preparing for surgeries.
Advantages of Ultrasound Compared to MRI
Although MRI excels at imaging soft tissues, CT scans provide clearer and quicker visualization of bones. This makes CT especially valuable for diagnosing Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2.
| Feature | CT Scan | MRI |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster imaging time | Slower imaging time |
| Availability | Widely available | Less accessible in smaller facilities |
| Bone Structure Analysis | Superior visualization of bone | Limited bone detail |
| Soft Tissue Evaluation | Adequate | Superior |
Radiological Indicators of Neurological Conditions
Radiology aids in understanding Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 by revealing how the brain and nerves are impacted, assisting doctors in diagnosis and prognosis.
Radiology reveals brain alterations vital for diagnosing neurological conditions, often highlighting malformations. MRI plays a crucial role in detecting these changes and guiding treatment planning.
Radiological Insights into Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2 Imaging reveals the extent of brain malformations in Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2, complicating diagnosis of neural conditions. A specialized team is essential for effective treatment and care. These scans assist clinicians in predicting prognosis and designing appropriate interventions.
Here are the key neurological findings in radiology:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Neuroanatomy Alterations | Characterized by cerebellar tonsil herniation and posterior fossa abnormalities. |
| Brain Malformations | Includes hydrocephalus , changes in spinal cord structure, and brainstem anomalies. |
| Neural Disorder Diagnosis | Relies on the identification of structural abnormalities and their correlation with clinical symptoms. |
These findings are crucial, as they influence patient treatment and future health outcomes. Advanced imaging techniques enable doctors to improve diagnosis and address brain malformations more effectively.
Understanding Ventriculomegaly in Type 2 Chiari Malformation
Ventriculomegaly is frequently observed in patients with Arnold Chiari Malformation Type 2, indicating enlarged brain ventricles. This often raises concerns about hydrocephalus, a significant complication requiring treatment.
Diagnostic Significance
Ventricle enlargement is crucial for detecting Chiari Malformation Type 2. MRI scans reveal enlarged ventricles, indicating potential hydrocephalus. Physicians rely on these images to confirm the diagnosis and assess severity.
This enables them to anticipate potential issues and predict the patient’s future needs.